Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) occur when the same part of the body is repeatedly subjected to stress.
Injuries of this nature are largely associated with office work. But an RSI can also develop with manual labor occupations requiring recurring stress and strain on the same joints, muscle groups, soft tissues, bones, or parts of the spine. Treatment will depend on the severity of the injury and the area that’s affected.
What Causes Repetitive Strain Injuries?
RSIs are often caused the repeated use of the same structures. For instance, carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is typically caused by repetitious wrist movements that irritate the median nerve that goes from the forearm to the hand. RSIs involving work-related tasks may also be caused by the use of vibrating machinery or equipment, consistently working in colder temperatures, regularly carrying heavy loads, or situations where the same posture or physical position is held for long periods of time. There’s also evidence that psychological stress may aggravate a repetitive strain injury.
How Can You Tell If You Have an RSI?
A repetitive strain injury often produces occasional discomfort that progressively gets works as stress is placed on the same area. It’s also common for certain movements to actions to trigger symptoms. If an RSI results in inflammation, nearby nerves may be irritated. Symptoms experienced may also include:
- Throbbing sensations or instances of severe pain
- Tenderness around the affect soft tissue or joint
- General weakness in the affected area
- Numbness or tingling sensations that extends to nearby areas
Diagnosis usually involves a discussion of symptoms and what types of movements a patient normally makes involving the affected area. If an RSI involves a musculoskeletal disorder, image tests that include X-rays, CT scans, ultrasound scans, or MRIs may be done to view the bones, joints, and soft tissues in the area that’s affected. If it’s believed nerve damage has occurred, testing may include nerve conduction studies or a nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test.
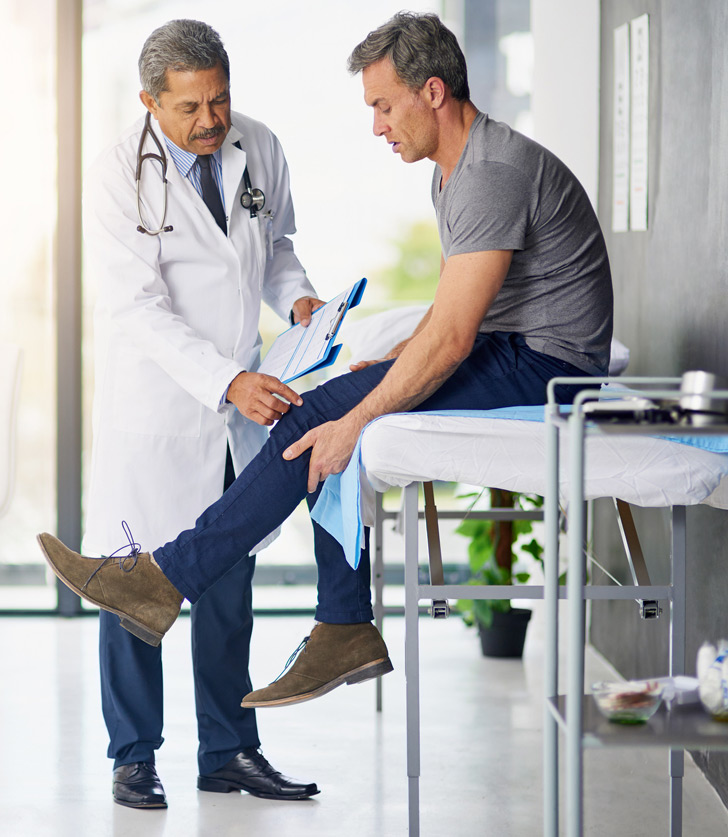

Treatment Options
Anti-inflammatory medications and over-the-counter or prescriptions may be recommended to manage symptoms related to an RSI. If a wrist or finger joint is affected, splinting may be recommended to minimize movement as tissues heal. Relief may also result from the application of heat or cold to the affected area, but direct skin contact should be avoided. Some repetitive strain injury sufferers also benefit from:
- Therapeutic exercises
- Massage therapy
- Steroid injections
- A customized physical therapy program
Surgery is usually a last resort treatment recommendation for a repetitive strain injury. But if other treatment attempts aren’t effective, surgery may be performed to correct damage to a joint, release certain tendons or ligaments, or correct nerve damage.
When repetitive strain injuries are affecting your ability to work, talk to an attorney to find out what your options are.
